

The experiment is repeated with V CE kept constant say 2V, 3V, 4V etc.A graph is drawn with V BE along X-axis and I B along Y-axis.The base current I B is noted in each step.The base voltage V BE is varied from zero by adjusting the rheostat Rh 1.The collector voltage V CE is kept constant (eg.The collector current (output current) I C is measured by the milliammeter (mA). The collector voltage (output voltage) V CE is varied using the rheostat Rh 2 and readings are noted from voltmeter V 2. The base current (input current) I B is measured using a microammeter (♚). The rheostat Rh 1 is used to vary base voltage (input voltage) V BE and it is read from voltmeter V1.Connections are made as shown in the circuit diagram.Students will be able to do the experiment, once they understand the procedure. The family of curves obtained by plotting I C against V CE for each value of I B is called output characteristics. This is repeated for increasing values of I B. The family of curve obtained by plotting I B against V BE for each V CE value is called input characteristics.īy keeping the base current (I B) constant, collector- emitter (V CE) voltage is varied and the corresponding I C values are obtained. This is repeated for increasing values of V CE. Keeping the collector- emitter (V CE) voltage constant, the base- emitter (V BE) voltage is increased from 0 and the corresponding base current (I B) values are noted.
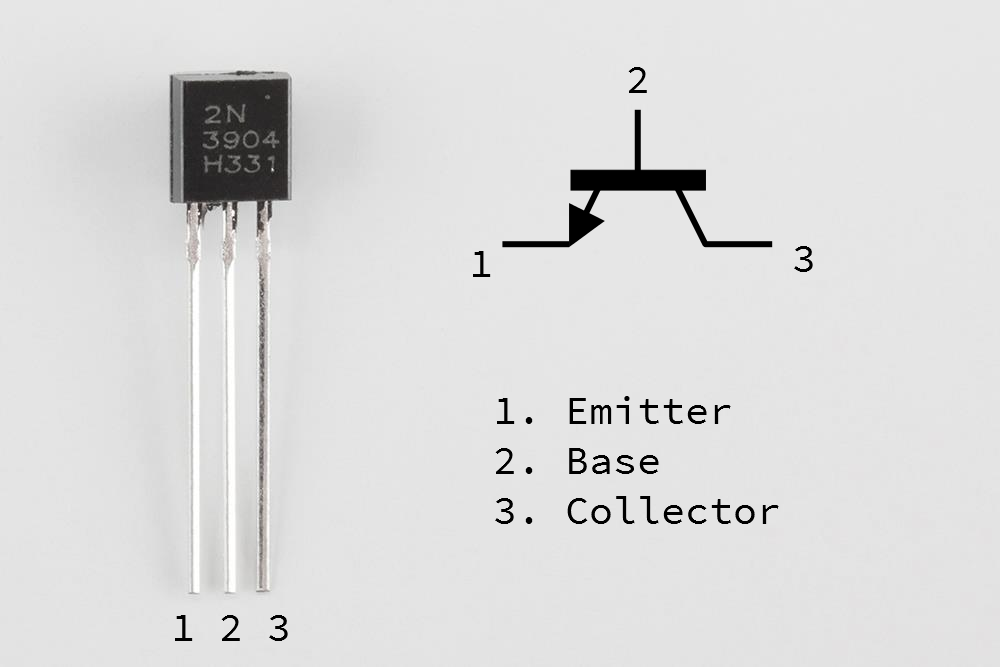
The circuit diagram for npn transistor is shown below. In pnp transistors, the majority current carriers are holes. The other type of charge,holes, are a minority. Electron flowing from the emitter to the collector forms the base of the majority of current flow through the transistor. A npn transistor is one in which the majority current carrier are electrons. Bipolar junction transistors come in two main types, npn and pnp. A small current entering in the base region of the transistor causes a much larger current flow from the emitter to the collector region. Because the controlled (output) power can be higher than the controlling (input) power, a transistor can amplify a signal.īipolar Junction Transistors are transistors which are made up of 3 regions, the base, the collector, and the emitter. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals changes the current through another pair of terminals. It is composed of semiconductor material with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. To study the static characteristic of a transistor (Common Emitter Configuration)Ī transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify or switch electronic signals and electrical power.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
